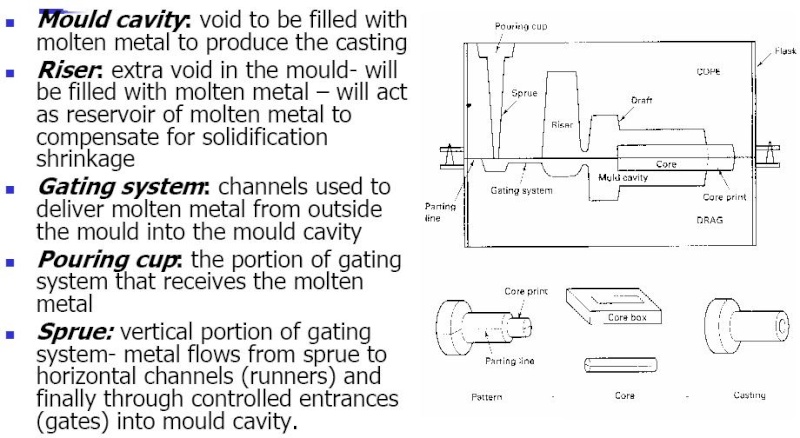
Metal Casting Processes
Casting Products

Principles of Solidificatio
Nucleation
Nucleation - The physical process by which a new phase is produced in a material.
Critical radius (r*) - The minimum size that must be formed by atoms clustering together in the liquid before the solid particle is stable and begins to grow.
Under cooling - The temperature to which the liquid metal must cool below the equilibrium freezing temperature before nucleation occurs.
Homogeneous Nucleation - Formation of a critically sized solid from the liquid by the clustering together of a large number of atoms at a high under cooling (without an external interface).
Heterogeneous Nucleation - Formation of a critically sized solid from the liquid on an impurity surface.
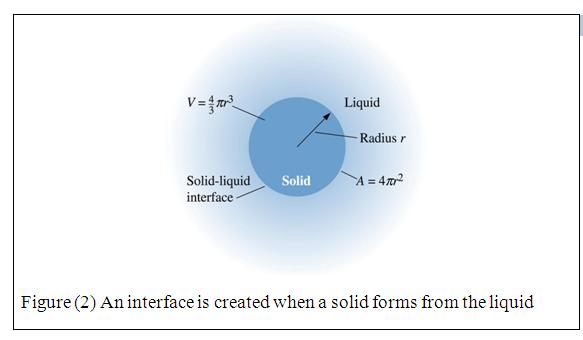
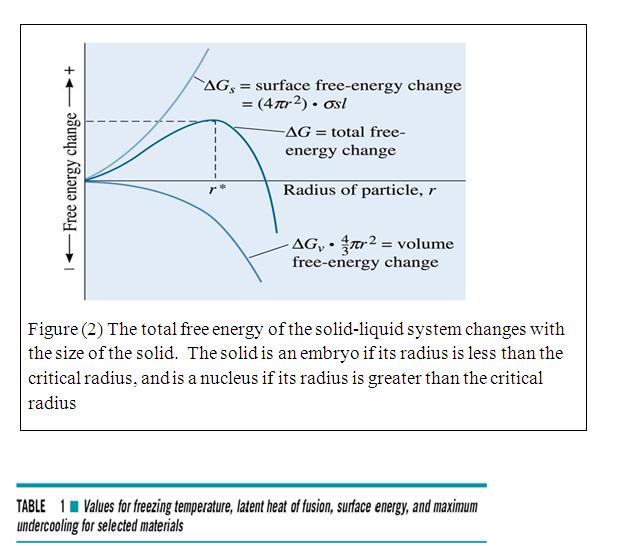

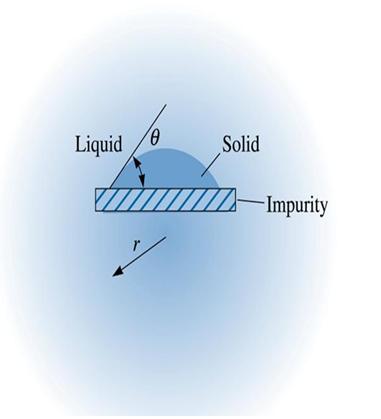
Figure (3) A solid forming on an impurity can assumed the critical radius with a smaller increase in the surface energy. Thus, heterogeneous nucleation can occur with relatively low under cooling’s
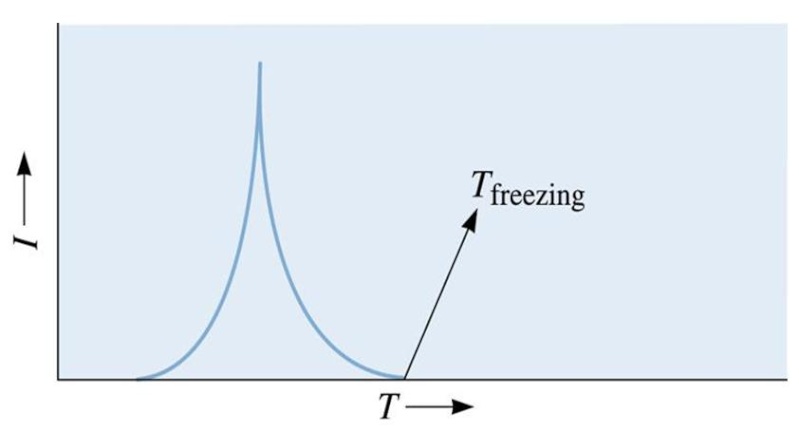
Figure (4) Rate of nucleation (l) as a function of temperature of the liquid (T)
Applications of Controlled Nucleation
Grain refinement - The addition of heterogeneous nuclei in a controlled manner to increase the number of grains in a casting.
Dispersion strengthening - Increase in strength of a metallic material by generating resistance to dislocation motion by the introduction of small clusters of a second material.
Solid-state phase transformation - A change in phase that occurs in the solid state.
Rapid solidification processing - Producing unique material structures by promoting unusually high cooling rates during solidification.
Specific heat - The heat required to change the temperature of a unit weight of the material one degree.
Solidification front - Interface between a solid and liquid.
Planar growth - The growth of a smooth solid-liquid interface during solidification, when no undercooling of the liquid is present.
Dendrite - The tree like structure of the solid that grows when an under cooled liquid solidifies.
Growth Mechanisms
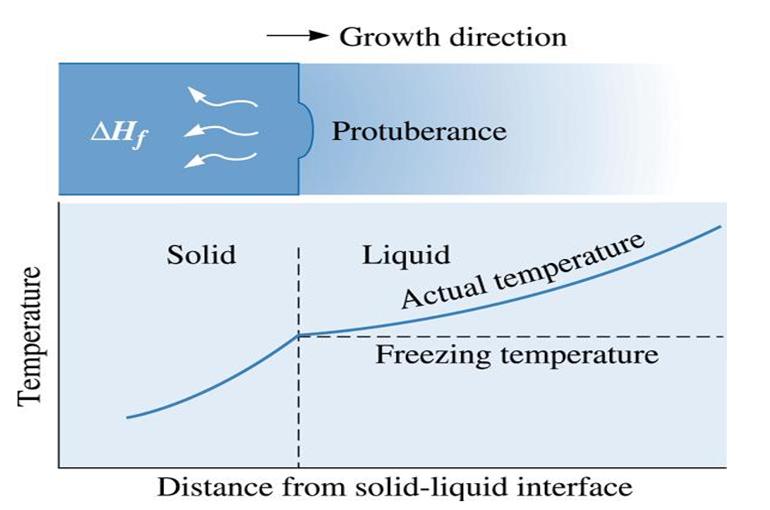
Figure (5) when the temperature of the liquid is above the freezing temperature a protuberance on the solid-liquid interface will not grow, leading to maintenance of a planer interface. Latent heat is removed from the interface through the solid
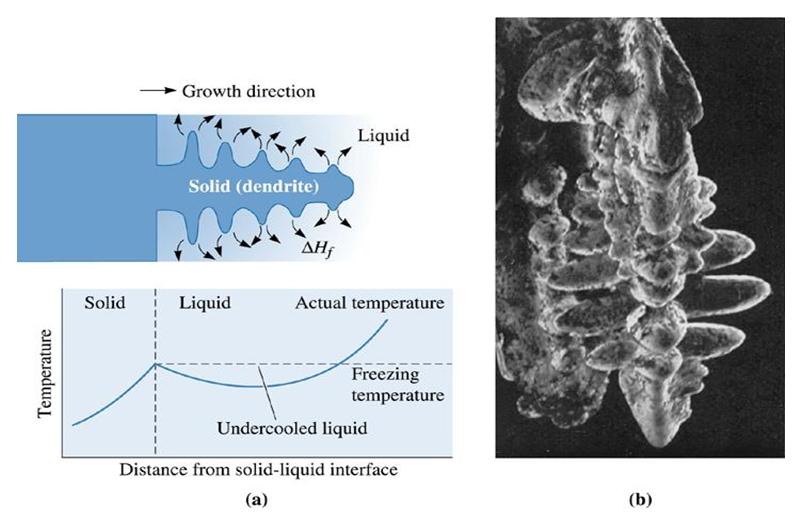
Figure (6) (a) If the liquid is undercooled, a protuberance on the solid-liquid interface can grow rapidly as a dendrite. The latent heat of fusion is removed by raising the temperature of the liquid back to the freezing temperature. (b) Scanning electron micrograph of dendrites in steel (x 15)
Solidification Time and Dendrite Size
Chvorinov’s rule - The solidification time of a casting is directly proportional to the square of the volume-to-surface area ratio of the casting.
Mold constant (B) - A characteristic constant in Chvorinov’s rule.
Secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS) - The distance between the centers of two adjacent secondary dendrite arms.
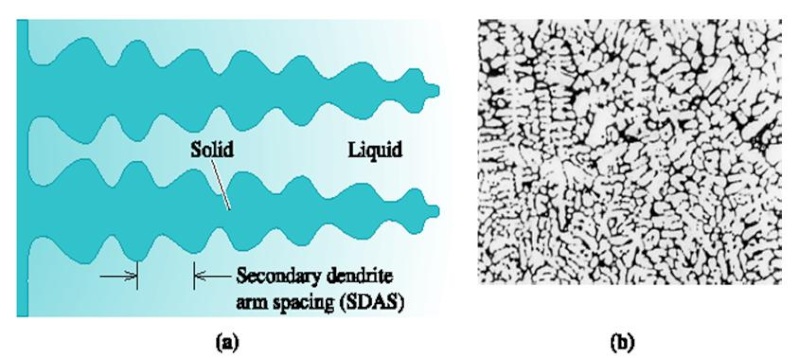
Figure (7) (a) The secondary dendrite arm spacing (SDAS). (b) Dendrites in an aluminum alloy (x 50). (From ASM Handbook, Vol. 9, Metallography and Microstructure (1985), ASM International, Materials Park, OH 44073-0002.)

Figure (

The effect of solidification time on the secondary dendrite arm spacings of copper, zinc and aluminum
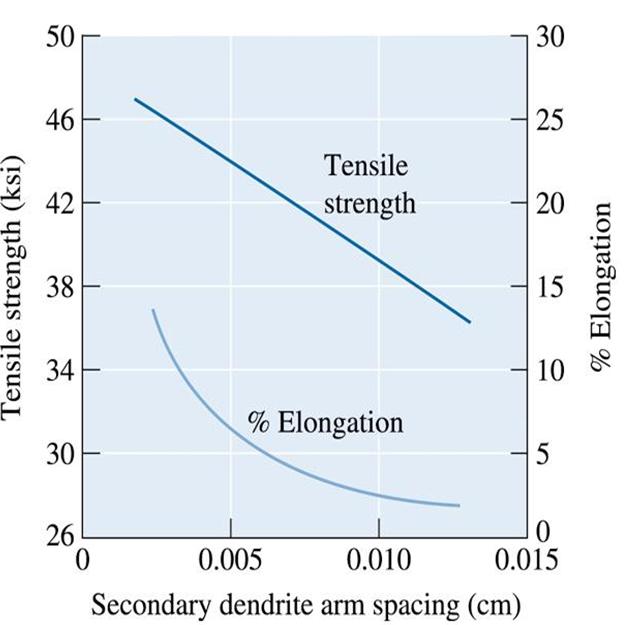
Figure (9) The effect of the secondary dendrite arm spacing on the properties of an aluminum casting alloy
Cooling Curves
Recalescence - The increase in temperature of an undercooled liquid metal as a result of the liberation of heat during nucleation.
Thermal arrest - A plateau on the cooling curve during the solidification of a material caused by the evolution of the latent heat of fusion during solidification.
Total solidification time - The time required for the casting to solidify completely after the casting has been poured.
Local solidification time - The time required for a particular location in a casting to solidify once nucleation has begun.
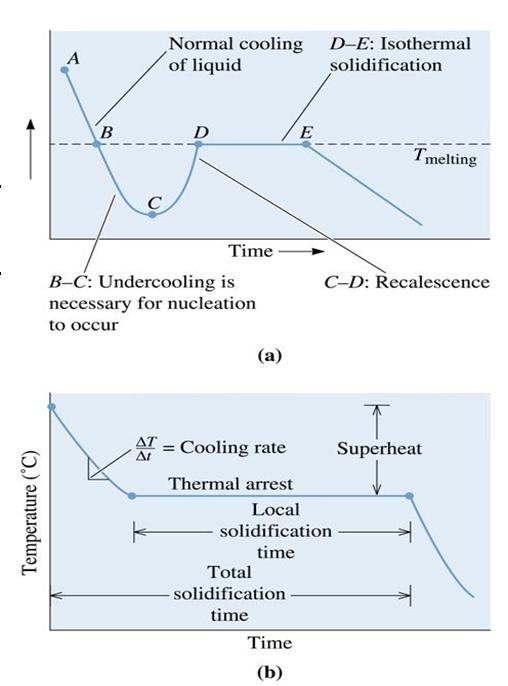
Figure (13) (a) Cooling curve for a pure metal that has not been well inoculated. Liquid cools as specific heat is removed (betweens points A and B). Undercooling is thus necessary (between points B and C). As the nucleation begins (point C), latent heat of fusion is released causing an increase in the temperature of the liquid. This process is known as recalescence (point C to point D). Metal continues to solidify at a constant temperature (T melting). At point E, solidification is complete. Solid casting continues to cool from the point. (b) Cooling curve for a well inoculated, but otherwise pure metal. No undercooling is needed. Recalescence is not observed. Solidification begins at the melting temperature.
+Cast Structure
Chill zone - A region of small randomly oriented grains that forms at the surface of a casting as a result of heterogeneous nucleation.
Columnar zone - A region of elongated grains having a preferred orientation that forms as a result of competitive growth during the solidification of a casting.
Equiaxed zone - A region of randomly oriented grains in the center of a casting produced as a result of widespread nucleation.
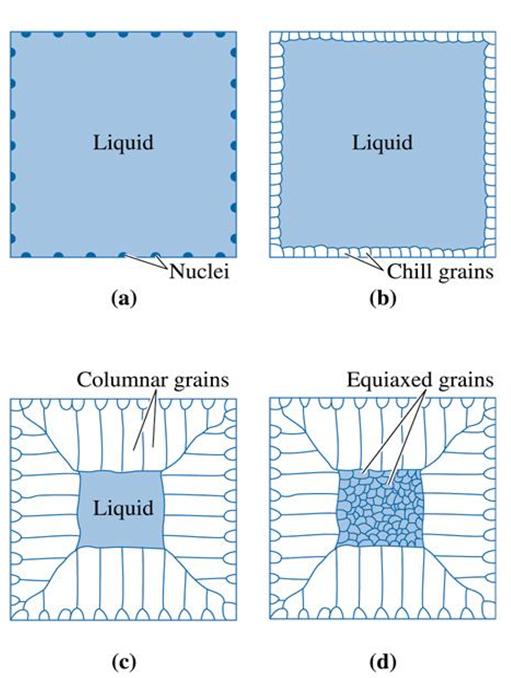
Figure (14) Development of the ingot structure of a casting during solidification: (a) Nucleation begins, (b) the chill zone forms, (c) preferred growth produces the columnar zone3, and (d) additional nucleation creates the equiaxed zone

Figure (15) Competitive growth of the grains in the chill zone results in only those grains with favorable orientations developing into columnar grains
Solidification Defects
Shrinkage - Contraction of a casting during solidification.
Micro-shrinkage- Small, frequently isolated pores between the dendrite arms formed by the shrinkage that accompanies solidification.
Gas porosity- Bubbles of gas trapped within a casting during solidification, caused by the lower solubility of the gas in the solid compared with that in the liquid.
Sievert’s law- The amount of a gas that dissolves in a metal is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas in the surroundings.
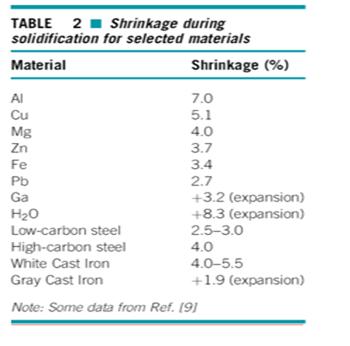
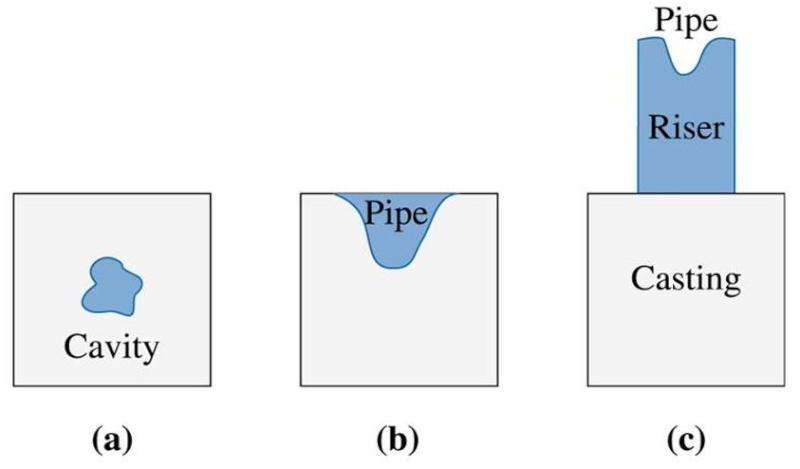
Figure (16) several types of macro-shrinkage can occur, including cavities and pipes. Risers can be used to help compensate for shrinkage

Figure (18) (a) Shrinkage can occur between the dendrite arms. (b) Small secondary dendrite arm spacings result in smaller, more evenly distributed shrinkage porosity. (c) Short primary arms can help avoid shrinkage. (d) Interdendritic shrinkage in an aluminum alloy is shown (x 80)
Casting Processes for Manufacturing Components
Sand casting - A casting process using sand molds.
Investment casting - A casting process that is used for making complex shapes such as turbine blades, also known as the lost wax process.
Lost foam process - A process in which a polymer foam is used as a pattern to produce a casting.
Permanent mold casting - A casting process in which a mold can be used many times.
Pressures die casting - A casting process in which molten metal/alloys is forced into a die under pressure.
Continuous casting - A process to convert molten metal or an alloy into a semi-finished product such as a slab.
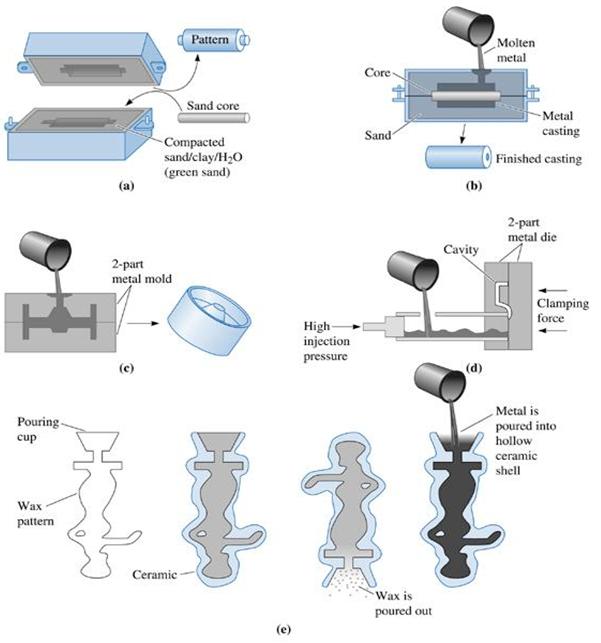
Figure (19) Four typical casting processes: (a) and (b) Green sand molding, in which clay-bonded sand is packed around a pattern. Sand cores can produce internal cavities in the casting. (c) The permanent mold process, in which ,metal is poured into an iron or steel mold. (d) Die casting, in which metal is injected at high pressure into a steel die. (e) Investment casting, in which a wax pattern is surrounded by a ceramic; after the wax is melted and drained, metal is poured into the mold

Figure (20) Engine block produced using the lost foam casting process. (Courtesy of Paul Arch, Nova Chemicals.)
Continuous Casting
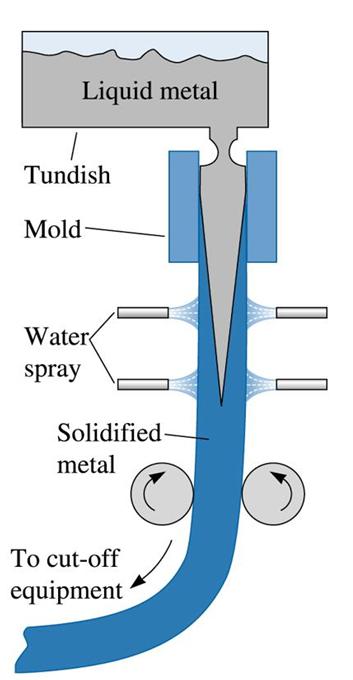
Figure (22) Vertical continuous casting, used in producing many steel products. Liquid metal contained in the tundish partially solidifies in a mold
Directional Solidification (DS), Single Crystal Growth, and Epitaxial Growth
Directional solidification (DS) - A solidification technique in which cooling in a given direction leads to preferential growth of grains in the opposite direction, leading to an anisotropic-oriented microstructure.
Bridgman processes - A process to grow semiconductor and other single crystals.
Epitaxial growth - Growth of a material via epitaxy.
Homoepitaxy - Growth of a highly oriented material onto a crystal of the same material.
Heteroepitaxy - Growth of a highly oriented material onto a different substrate material.
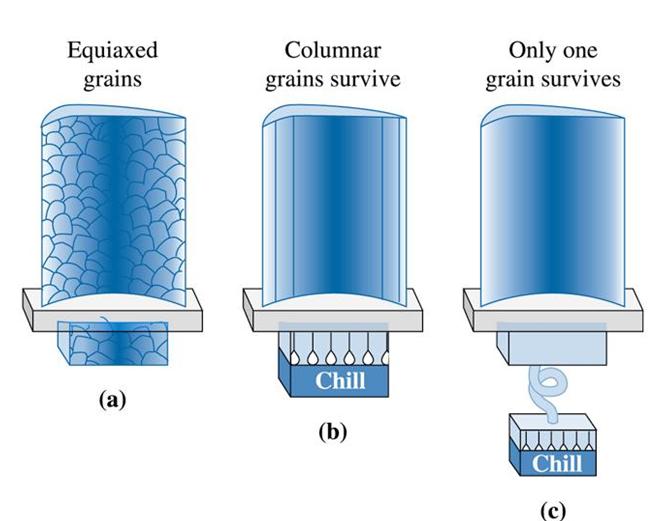
Figure (25) Controlling grain structure in turbine blades: (a) conventional equiaxed grains, (b) directionally solidified columnar grains, and (C) single crystal.
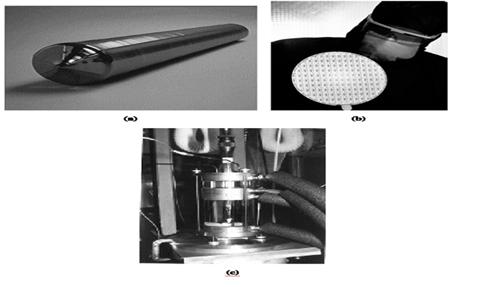
Figure (26) (a) Silicon single crystal, (b) silicon wafer, and (c) Bridgman technique.
Basic Requriments of Casting Processes